 |
| Click diagram to enlarge |
Last update: 7 May 2025 8:50 UTC
(this post is being periodically updated with new reentry forecasts)
* The current nominal forecast is reentry on 10 May 2025, 7:51 UTC ± 20.6 hr *
In the second week of May 2025, an unusual object will reenter. It concerns the Kosmos 482 Descent Craft (1972-023E, cat. nr. 6073).
This object is the lander module from a 1972 failed Soviet Venera mission to Venus. Because of a failure of the upper stage of the rocket that launched it, it got stuck in a very elliptical orbit around Earth in 1972, instead of going to Venus.
I published an extended discussion and analysis of this object and its history
three years ago in The Space Review. The identification of this object as the lander module was initially suggested by Jonathan McDowell (see his brief interesting history
here).
Recently declassified
Russian historic documents unearthed by Anatoly Zak point out that after failure to get to a heliocentric orbit, the lander was deliberately separated from the main bus by the spacecraft operators.
My analysis published in 2022 suggests that this happened in June 1972. The lander is encased in a semi-spherical shaped Titanium protective shell, a kind of rounded metal bucket so you will (see image below).
As this is a
lander that was
designed to survive passage through the Venus atmosphere, it is possible that it will survive reentry through the Earth atmosphere intact, and
impact intact. It likely will be a hard impact: I doubt the parachute deployment system will still work after 53 years and with dead batteries. There are many uncertain factors in whether the lander will survive reentry though, including that this will be a long shallow reentry trajectory, and the age of the object.
 |
| Venera 7 lander mock-up. The Kosmos 482 Descent Craft is probably similar. Photo: NASA |
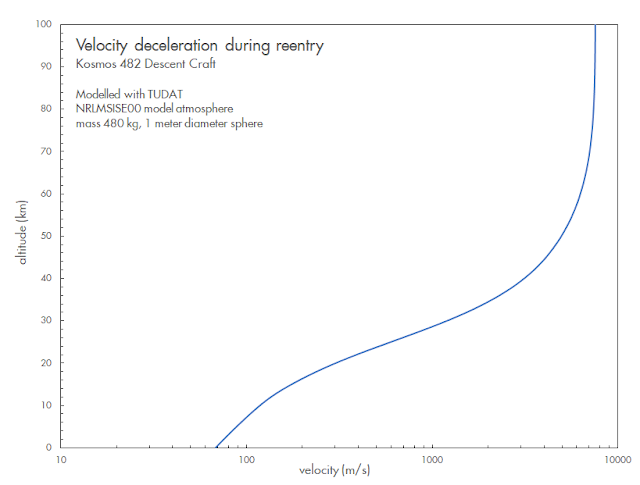
The risks involved are not particularly high, but not zero: with a mass of just under 500 kg and 1-meter size, risks are somewhat similar to that of a meteorite impact. A TUDAT reentry analysis to ground level suggests an
impact speed (after atmospheric deceleration) of about
65-70 meter per second (~242 km/h), assuming the reentering lander did not break up or extensively ablate during reentry (see the diagram below: note the logarithmic scale of the x-axis). The kinetic energy at impact is similar to that of a 40-55 cm large (after ablation) meteorite fragment. As it will likely reach earth surface as only one single object, the risks involved are lower than for example those created by a Falcon 9 upper stage reentry, which showers multiple meter-sized objects over a large area (
as we saw recently with the impact of Falcon 9 remains in Poland).
 |
| Click diagram to enlarge |
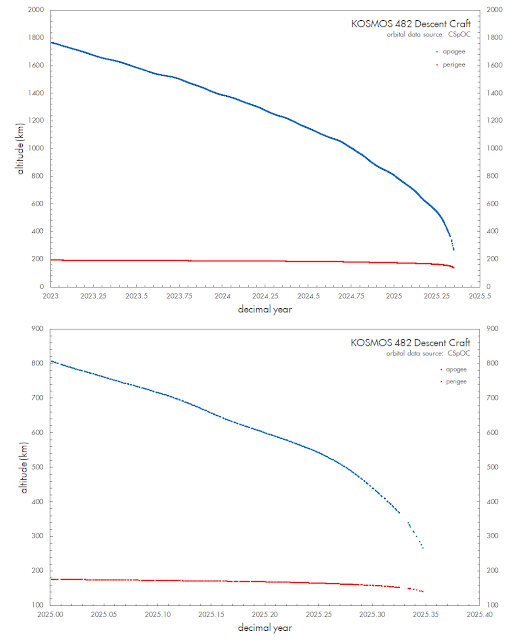
The diagrams below shows the change in altitude of apogee and perigee over the past 1.5 years and the past 4 months: notably apogee has been coming down steadily, but in the past few months, perigee has started to come down too. Late on May 6, the object was in a 268 x 141 km orbit, with apogee coming down by 17 km/day and perigee by 3 km/day (and these values increasing each day).
 |
| Click diagram to enlarge |
 |
| Click diagrams to enlarge |
The reentry is an uncontrolled reentry. At the moment, we cannot say with any degree of certainty when and where the Kosmos 482 Descent Craft exactly will reenter.
With an orbital inclination of
51.95 degrees [note: I initially erroneously stated 51.7 here], the reentry can occur
anywhere between latitude 52 N and 52 S, and from our current modelling (see below) the reentry should happen on or near May 10th, 2025 (but this is dependent on a.o. how solar activity develops in the coming days), give or take a day. The uncertainty in the reentry date will be (and is) decreasing once we will get closer to the actual reentry, but even on the day itself uncertainties will remain large.
Over the past months, together with my colleague Dominic Dirkx, we have been developing a reentry model for this object in TUDAT.
TUDAT, the
TU Delft Astrodynamics Toolbox is
open source, multi-platform Astrodynamics software developed and maintained at
the Aerospace faculty of Delft University of Technology (TU Delft) in the Netherlands (where I work). The TUDAT script we use for our analysis
is here, while the TUDAT software itself
is available here.
The Kosmos 482 Descent Craft is probably similar to the descent craft of Venera 8 (which was launched only a few days earlier in 1972). Literature values suggest that the object is about 1 meter in size and semi-globular, with a mass of ~495 kg.
Using our TUDAT model and a 1-meter diameter, and the NRLMSISE00 model atmosphere with historic space weather data, we find that the orbital evolution of the object from mid-1972 to early 2025 is actually best matched when we use a mass of 480 kg, 15 kg less than the literature value. All our forecast predictions are therefore done using a mass of 480 kg.
For our forecasts we employ the NRLMSISE00 model atmosphere, and historic spaceweather data plus estimated future space weather (solar flux). Orbit updates for each run are sourced from the US Military tracking network
CSpOC (so as a note: our forecasts are
not based on our own tracking data. They are based on our own custom reentry model developed at Delft University of Technology, with external tracking data from CSpOC as input).
 |
| Click diagram to enlarge |
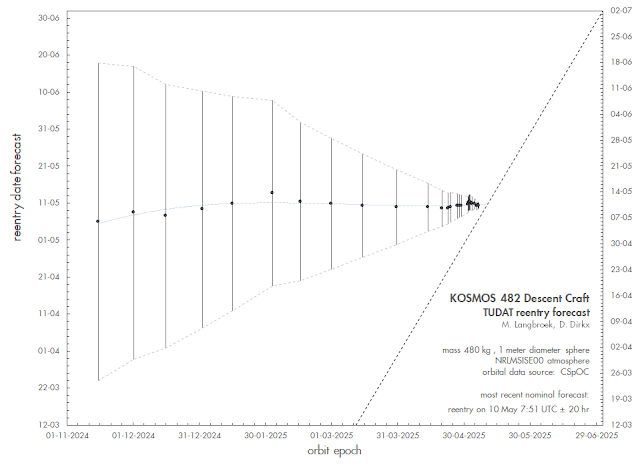
The diagrams in top of this post and below (which I will periodically update) give the evolution of our reentry predictions, based on orbits issued for the object since November 2024. Over the past half year, the model has consistently pointed to reentry within a few days of 9-10 May 2025.
The latest nominal forecasts currently center on May 10, but are still fluctuating with each orbital update. Early May, there was a short-lived tendency in the model runs of a shift towards a later time of reentry (i.e. May 11 rather than May 10), as can be seen in the below diagrams and the table near the end of this post. But lately, the new forecast runs are returning to nominally May 10.
 |
| Click diagram to enlarge |
 |
| Click diagram to enlarge |
The brief shift towards a later date in the early May model runs was due to space weather forecasts underestimating future solar activity at that time. I had started to note this (when comparing earlier forecast solar flux values to actual solar flux values for the last days of April and the first days of May) and already expected the nominal forecasts to return to May 10, as they now indeed do.
This highlights the influence of the uncertainties in estimated future solar activity on the forecasts. Future solar activity is not well predictable. Even the best reentry models will be off in their forecast if actual solar activity in the window between the moment of forecast and the moment of reentry develops differently than the predictions. Solar flux variations are an important driving factor of short-term variations in density and extent of the upper atmosphere. The latter determine how many drag the object experiences over its orbit, and with that how quick the orbit decays. Stronger solar activity will mean an earlier reentry, lower solar activity a later reentry.
Of course, at this point the uncertainty in the forecast is still +/- 0.9 days. The forecast is currently best expressed as a two-day reentry window, i.e. between early May 9 and early May 11, rather than pinpointing one specific day.
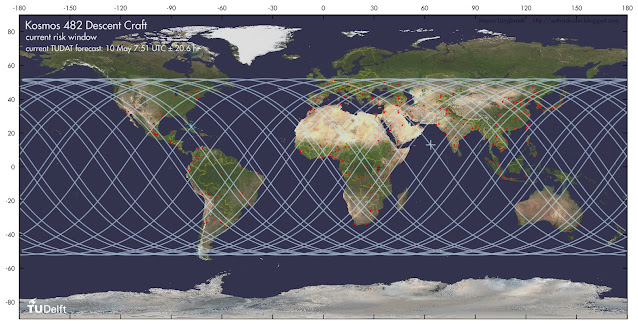
The map below gives the trajectory of the object over the current uncertainty window of the TUDAT reentry forecast (red dots are cities with over 1 million inhabitants):
 |
| Click map to enlarge |
CSpOC, the US military tracking network, has started to provide TIP (Time of Impact Prediction) messages for the object on May 6. They are depicted as red circles in the diagram below.
The current CSpOC TIP is forecasting reentry at 9 May 23:58 ± 15 hr UTC. This is somewhat earlier than our TUDAT model currently has it (10 May 7:51 ± 20.6 hr UTC), as can be seen in the diagram below (open red dots are CSpOC TIP; solid black dots are TUDAT forecasts). This could be due to our model still being influenced by solar activity being lower than predicted for the current and coming days.
Below is the evolution of the reentry forecast in tabular form, latest forecast at the bottom. Please take note of the uncertainty values listed in the last column!
--------------------------------------------------------------------
TUDAT REENTRY FORECAST EVOLUTION for KOSMOS 482 Descent Craft
M. Langbroek & D. Dirkx, Delft University of Technology
Date/times in UTC
REFERENCE ORBIT ORBIT EPOCH REENTRY FORECAST +/-
----------------------------------------------------------------
15-11-2024 05:43 24320.23870400 05-05-2025 23:33 42.9 day
01-12-2024 05:32 24336.23116452 08-05-2025 09:09 39.5 days
15-12-2024 18:58 24350.79080401 07-05-2025 11:51 35.7 days
01-01-2025 11:20 25001.47260254 09-05-2025 07:20 32.0 days
15-01-2025 03:23 25015.14140884 10-05-2025 20:40 28.9 days
02-02-2025 08:54 25033.37115746 13-05-2025 17:52 25.1 days
15-02-2025 03:20 25046.13941015 11-05-2025 09:52 21.3 days
01-03-2025 00:07 25060.00535989 10-05-2025 17:51 17.7 days
15-03-2025 05:56 25074.24770046 10-05-2025 07:57 14.0 days
30-03-2025 12:05 25089.50360681 09-05-2025 21:11 10.1 days
13-04-2025 21:32 25103.89775709 09-05-2025 22:01 6.5 days
20-04-2025 01:39 25110.06916305 09-05-2025 11:31 4.9 days
22-04-2025 21:24 25112.89204293 09-05-2025 12:48 4.2 days
23-04-2025 22:57 25113.95657237 09-05-2025 19:43 4.0 days
27-04-2025 00:27 25117.01893077 10-05-2025 04:52 3.3 days
28-04-2025 00:24 25118.01685903 10-05-2025 06:33 3.1 days
28-04-2025 22:50 25118.95143786 10-05-2025 06:01 2.8 days
01-05-2025 20:57 25121.87323063 10-05-2025 14:30 2.2 days
02-05-2025 09:12 25122.38386703 11-05-2025 02:36 2.2 days
02-05-2025 12:16 25122.51167762 11-05-2025 03:41 2.2 days
02-05-2025 17:52 25122.74476620 11-05-2025 06:50 2.1 days
03-05-2025 18:07 25123.75533175 10-05-2025 20:48 1.8 days
03-05-2025 21:05 25123.87876286 10-05-2025 23:06 1.8 days
04-05-2025 20:47 25124.86648285 10-05-2025 19:05 1.5 days
05-05-2025 20:29 25125.85361170 10-05-2025 07:26 1.1 days
06-05-2025 09:39 25126.40254557 10-05-2025 08:37 1.0 day
06-05-2025 21:26 25126.89335737 10-05-2025 07:51 20.6 hr *
I will periodically update this table with new forecasts, more frequently so when the reentry dates comes nearer.
Here is footage I shot of the Kosmos 482 Descent Craft with my tracking camera in Leiden, in 2020:
An added note: about that parachute....
To muddy the waters further, a story is spreading that the parachute of the landing craft might already have deployed in space. This is based on telescopic imagery purportedly showing this.
I have strong doubts that the imagery in question shows any meaningful detail. The imagery has the same origin, and the same problems attached, as the imagery I discussed in 2022 in my Space Review article. I think the "detail" is the result of camera/telescope shake and atmospheric distortion.
This post has been updated with new forecasts and additional background information several times








No comments:
Post a Comment